However, by reifying variables, Algol 50 permits writing programs in a way that permits regarding programs in this fragment of Algol 60 as just sugared versions of Algol 50 programs.
Instead of writing var(t) for some variable var, we
write ![]() , where
, where ![]() is a state vector giving
the values of all the variables. In the above program, we'll
have
is a state vector giving
the values of all the variables. In the above program, we'll
have ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
The variables of the Algol 60 program correspond to functions of time in the above first Algol 50 version and become distinct constant symbols in the version of Algol 50 with reified variables. Their distinctness is made explicit by the ``unique names'' axiom
![]()
In expressing the program we use the assignment and
contents functions, ![]() and
and ![]() , of
(McCarthy 1963) and (McCarthy and Painter 1967).
, of
(McCarthy 1963) and (McCarthy and Painter 1967).
![]() is the new state
is the new state ![]() that results when the
variable var is assigned the value value in state
that results when the
variable var is assigned the value value in state ![]() .
.
![]() is the value of var in state
is the value of var in state ![]() .
.
As described in those papers the functions a and c satisfy the axioms.
![]()
![]()
![]()
and
![]()
The following function definitions shorten the expression of programs. Note that they are just function definitions and not special constructs.
![]()
![]()
We make the further abbreviation loop = start+2 specially for this program, and with this notation our program becomes
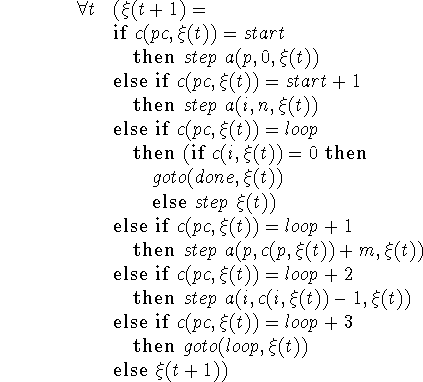
In Algol 50, the consequents of the clauses of the conditional expression are in 1-1 correspondence with the statements of the corresponding Algol 60 program. Therefore, the Algol 60 program can be regarded as an abbreviation of the corresponding Algol 50 program. The (operational) semantics of the Algol 60 program is then given by the sentence expressing the corresponding Algol 50 program together with the axioms describing the data domain, which in this case would be the Peano axioms for natural numbers. The transformation to go from Algol 60 to Algol 50 would be entirely local, i.e. statement by statement, were it not for the need to use statement numbers explicitly in Algol 50.
Program fragments can be combined into larger fragments by taking the conjunction of the sentences representing them, identifying labels where this is wanted to achieve a go to from one fragment to another and adding sentences to make sure that the program counter ranges don't overlap.
The correctness of the Algol 50 program for multiplication by addition is expressed by
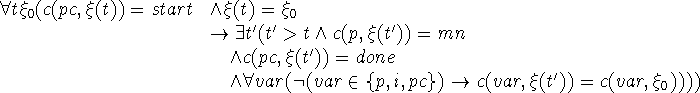
Note that we quantify over all initial state vectors. The last part of the correctness formula states that the program fragment doesn't alter the state vector other than by altering p, i and pc.
We have not carried the Algol 50 idea far enough to verify that all of Algol 60 is conveniently representable in the same style, but no fundamental difficulties are apparent. In treating recursive procedures, a stack can be introduced, but it would be more elegant to do without it by explicitly saying that the return is to the statement after the corresponding procedure call and variables are restored to their values at the time of the call. This requires the ability to parse the past, needed also for Elephant 2000.
We advocate an extended Algol 50 for expressing the operational semantics of Algol-like programming languages, i.e. for describing the sequence of events that occurs when the program is executed. However, our present application is just to illustrate in a simpler setting some features that Elephant will require. In particular, proper treatment of calling a function procedure with side-effects will require a state that can have a value during the evaluation of an expression.
Nissim Francez and Amir Pnueli (see references) used an explicit time for similar purposes. Unfortunately, they abandoned it for temporal logic. While some kinds of temporal logic are decidable, temporal logic is too weak to express many important properties of programs.